The Swedish legal publisher Notisum AB has been on the Swedish market for online legal publishing since 1996. Our Internet-based law book at www.notisum.se is read by more than 50,000 persons per week and our customers range from municipalities and government institutions to Swedish multinationals.
The Swedish legal publisher Notisum AB has been on the Swedish market for online legal publishing since 1996. Our Internet-based law book at www.notisum.se is read by more than 50,000 persons per week and our customers range from municipalities and government institutions to Swedish multinationals.
Now we are heading for China, and I would like to share with you some practical experiences from this highly dynamic market and our challenges in trying to conquer it.
The case for a legal monitoring tool, codenamed “EnviTool”
In close co-operation with our customers, we had developed a set of specialized Internet based tools in Sweden for supporting the process of legal compliance and legal information sharing within big organizations. The key driver of these needs was the growing number of certificates according to the international environmental management standard ISO 14001:2004.
ISO 14001 is a worldwide industry standard to help companies to improve their environmental performance through the implementation of an environmental management system. There is much to say about management systems. Continuous improvement is the heart of the matter–it is all about doing the right things right. Establish a plan, do what you planned, check your results and then start all over by correcting your plans. Plan, Do, Check, Act.
through the implementation of an environmental management system. There is much to say about management systems. Continuous improvement is the heart of the matter–it is all about doing the right things right. Establish a plan, do what you planned, check your results and then start all over by correcting your plans. Plan, Do, Check, Act.
According to the standard, you have to identify the relevant environmental legislation for your organization. You need access to those laws and regulations, and you have to keep an updated list. You should also make the information available to the people of your organization.
By providing an online legal register, monitored for changes, with a whole set of information sharing and workflow features, Notisum helps the certified companies to comply with the environmental legislation.
We developed this system step by step. When it came to going outside the borders of the Kingdom of Sweden, we changed the name from Rättsnätet+Miljö to EnviTool.
The case for China
Sweden is a country of very high penetration of the ISO 14001 standard, and the use of the standard is in a mature phase in most organizations. China, on the other hand, is number one in the world, with more than 70,000 certificates issued. The growth is double-digit. So China is the place to be if you have products for this specific customer group. The users of the standard are yet immature in China, so we knew there were some challenges out there.
The market for legal information tools is overall immature in China and legal compliance is not always on top of the manager’s priority lists. However, Notisum took the first steps, starting in 2009, to take on the challenge to make China our second home market. Many challenges, expected and unexpected, were waiting for EnviTool.
Step one – the product
Like many commercial ventures, the EnviTool project was the result of a randomly started chain of events. Our Swedish CEO was playing golf with a professor at KTH, the Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm. The professor was in charge of a student exchange program between National University of Singapore (NUS) and KTH. We were asked to host an internship for an ambitious computer science student in our company for one academic year.
The internship was successful, our student was doing a great job and we learned a lot about Asia and the Chinese culture. We have now hosted three excellent NUS students from Singapore, all good representatives of their university and their country. And all of them bilingual English and Chinese. That’s when we decided that China would be an interesting market to try. And yes – China is far away from Sweden, it is terribly big and it was really too large a challenge for our company. We wanted to try anyway, with the hope that Singapore could be the bridge for us.
We decided to start a subsidiary in Singapore and so we did. It is easy, by the way. According to the World Bank, Singapore ranks number one in the world in ease of doing business. Coming from Sweden, ranked number 50 in the world in terms of how easily you pay your taxes, I had an almost religious moment when we got a letter of gratitude from the Singaporean tax authorities after paying our taxes. Not so in Sweden, I may add…
With the first NUS intern now as our first employee, we started translating and adapting our internet tool together with our development manager in Sweden. The technological challenges were there, of course. We base our technology on the Microsoft.NET platform, but the support for the simplified Chinese character set was not totally implemented everywhere. Multi-language support was developed, and plenty were the occasions in the beginning when Swedish words popped up unexpectedly. The search function in Chinese is different in EnviTool and the relations between the legislative documents were so different from the Swedish and European law that we had to re-design our database structure.
Step two – the market research
With good help from the Swedish Trade Council in China, we did market research to see if there could be a similar market in China and if our business model could work.
After three journeys and two projects together with the trade council, we decided to give it a try. The EnviTool China project was about to take off. Learning to eat properly with chopsticks was part of the experience. Learning to appreciate the Chinese food was easier although there are some zoological challenges there too, outside the scope of this blog entry.
 At this point in time we also employed a Chinese/Swedish project manager with extensive knowledge and experience in the field.
At this point in time we also employed a Chinese/Swedish project manager with extensive knowledge and experience in the field.
Step three – the content
Translating the tool to Chinese and English was the easy part. When it came to the content, we had to throw out everything from Sweden and put in Chinese legislation and comments. We soon found interesting challenges.
Our first experience of the Chinese legal tradition,which is in many ways different from where we come from, was the search for a standard for citations. In the Swedish databases we had successfully used computer software to automatically find citations, law titles, cross references and other document data. It became clear to us that there were no shortcuts in the Chinese material. We had to input all data manually.
We decided to restrict the information to cover relevant legislation in the EHS (Environmental, Health & Safety) and CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) field and to concentrate on the national level with some provincial/municipal areas like Beijing and Shanghai. The EHS/CSR users are professionals in their field of work and their industries. They are not lawyers and not very used to legal information systems. EnviTool were developed with EHS/CSR managers in our minds. We wrote the editorial content to suit the needs of our target audience.
We realized that we needed a partner in China to provide fast and timely information. In ChinaLawInfo, established by Peking University in association with the university’s Legal Information Center, we found a great partner. They are the most important legal information provider in China and we saw that Notisum of Sweden and ChinaLawInfo had many similarities in experience and way of working. Yes, we are small and they are big, but that goes for Sweden and China all over. So EnviTool now provides the EHS/CSR laws and regulations from both ChinaLawInfo and government sources. We also have an on-going editorial co-operation in Beijing.
By now we also had good content. The EnviTool Internet service and database, provided from our Singapore company servers, were released in its first version in the fall of 2010.
Step four – market introduction
If company start-up was a short track in Singapore, it was a longer journey in the world’s second biggest economy. After having tried 50 other names, Envitool finally was translated to 安纬同 in Chinese and we got the business permit in August 2011.
We employed the people we needed and found a partner to help us with HR and finance issues. Since then we have started our sales and marketing activities, moving slowly forward. The use of legal information tools served from Singapore is combined with management consulting from our team in Shanghai. We provide training in using the tool and can assist the clients in finding the laws and regulations relevant to their operation.
The second generation of the site is up and running at www.envitool.com and we are proud to have customers from China, the US, Japan and four different European countries.
What we have learned and what we think of the future
To get to know China and the Chinese people is of course one part of the fun. Being a European, you make many mistakes, sometimes because of language, sometimes cultural.
One example of this confusion was when I intervened in the editorial process. In EnviTool we provide bi-lingual Chinese/English short and long comments to laws and regulations. In the Swedish service, which I am more familiar with, the short comment is rendered in italics with the longer comment below in plain text. In the English version of the comments in EnviTool, the short one was not in italics. I complained and our programmer quickly changed this. Shortly thereafter, at a customer meeting, I showed the comments, now in Chinese language version. (I don’t understand a word of Chinese.) Can you imagine Chinese characters in italics? I can tell you, it makes no sense and it looks bad. That was the language mistake. The cultural mistake was managerial. A Swedish employee would have told me how stupid I were, if I came up with such a bad idea. The Asian employee (highly intelligent and highly educated) probably saw the problem and maybe thought “the boss is more stupid than usual, but he is my boss so I have better do what he tells me!”. A lot to learn,  many aspects to consider.
many aspects to consider.
To conclude, the start-up was a bit slow because of the red tape but so far, our government contacts have been smooth. We have felt very welcome at the Chinese authorities like the Ministry of Environmental Protection and local governments. In the end, our goals are similar: better environmental and occupational health & safety legal compliance – better environment and better life for the citizens.
We know it will take a long time for us to get the knowledge and experience needed to be a significant player in the Chinese market, and we are prepared to stay there and step by step build our presence. It took many years to build a loyal and substantial customer base in Sweden. It will take even longer in China.
 Magnus Svernlöv is the founder and chairman of the Swedish online legal publisher Notisum (www.notisum.se) and its Chinese subsidiary Envitool (www.envitool.cn). He holds an MBA from INSEAD, France, a MScEE degree from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden and a BA from the School of Business, Ecnomics and Law, University of Gothenburg, Sweden. He welcomes any comment or feedback to ms@notisum.se
Magnus Svernlöv is the founder and chairman of the Swedish online legal publisher Notisum (www.notisum.se) and its Chinese subsidiary Envitool (www.envitool.cn). He holds an MBA from INSEAD, France, a MScEE degree from Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden and a BA from the School of Business, Ecnomics and Law, University of Gothenburg, Sweden. He welcomes any comment or feedback to ms@notisum.se
VoxPopuLII is edited by Judith Pratt. Editors-in-Chief are Stephanie Davidson and Christine Kirchberger, to whom queries should be directed. The information above should not be considered legal advice. If you require legal representation, please consult a lawyer.






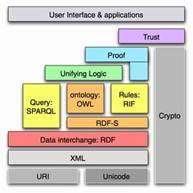
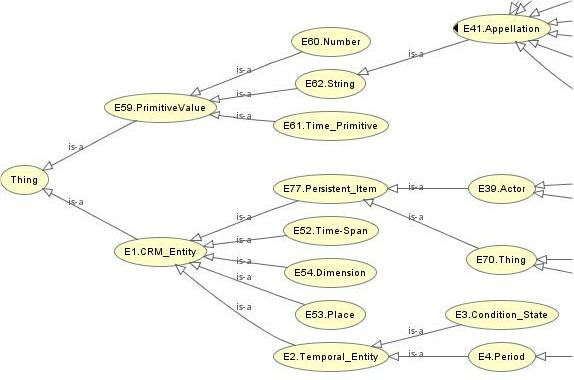
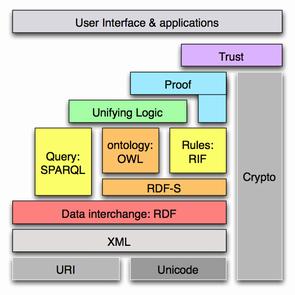
 Such ontologies usually include references to the concepts of Norm, Legal Act, and Legal Person, and may contain the formalization of
Such ontologies usually include references to the concepts of Norm, Legal Act, and Legal Person, and may contain the formalization of  In this regard, at
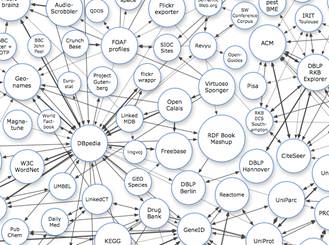
In this regard, at  Current research is focused on overcoming these problems through the establishment of gold standards in concept extraction and ontology learning from texts, and the idea of
Current research is focused on overcoming these problems through the establishment of gold standards in concept extraction and ontology learning from texts, and the idea of  and the relationships between legal ontology and legal epistemology, legal knowledge and common sense or world knowledge, expert and layperson’s knowledge, legal information and Linked Data possibilities, and legal dogmatics and political science (e.g., in
and the relationships between legal ontology and legal epistemology, legal knowledge and common sense or world knowledge, expert and layperson’s knowledge, legal information and Linked Data possibilities, and legal dogmatics and political science (e.g., in